Kubernetes cluster architecture : introduction
Kubernetes cluster architecture is a complex subject. Here we will try to clarify the concepts and make it easy to understand for beginners.
A node is a machine (virtual machine or a real machine)
If you have an application running in a single node and the
node goes down, the application goes offline and this incurs a loss of money.
This is why we deploy our app in a cluster which is a set of
nodes : if a node fails, the other nodes will execute the app and there
will not be a service interrupt.
In kubernetes, there are master nodes and a set of worker
nodes. A master node manages the worker nodes (it is responsible for the
distribution of the traffic between the worker nodes, replaces a worker node
which goes down, orchestrates the containers running inside the nodes, etc).
A masternode is a node that has kubernetes installed in it
and it is configured as a masternode.
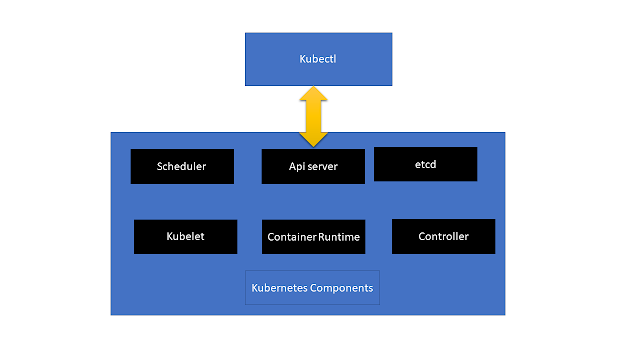
Roles of kubernetes components :
The Kubectl command line interface communicates with the api
server.
etcd : is a key value store used to store the data
needed to manage the cluster.
Scheduler: is responsible for distributing the containers
across multiple nodes.
The controller: is responsible for adding containers and
removing them.
Container runtime is the runtime necessary to run containers
(docker)
Kubelet : is the agent running on each node in the
cluster. It is responsible for monitoring the containers and checking if they
are running as expected.
Masternode vs worker node
This diagram shows the components explained above and their distribution on nodes.
This differs depending on whether the node is a master node or a worker node.
This kubernetes architecture tutorial for beginners arrives at its end.
If you want to deep dive into kubernetes, you can check our kubernetes pod tutorial or our kubernetes replicaset tutorial.
To check our other tutorials, you can like our how to program facebook page.




Post a Comment